 400-616-8800
400-616-8800 400-616-8800
400-616-8800
A-level 微积分之函数凹凸性
Concavity
凹凸性
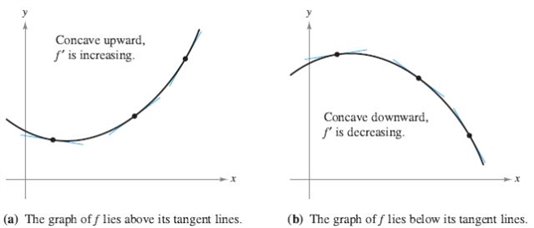
Let f be differentiable on an open interval I. If f' is increasing on I, then f is concave up on I. If f' is decreasing on I, then f is concave down on I.
函数在区间 I上处处可导,如果一阶导数增大,则函数为上凹的(concave up),如果一阶导数减小,则函数是是上凸的(concave down)。
The Second derivative and Concavity
Suppose that f'' exists on an open interval I.
• If f'' >0 on I, then f is concave up on I.
• If f'' < 0 on I, then f is concave down on I.
• If c is a point of I at which f'' changes sign at c (from positive to negative, or vice versa), then f has an inflection point at c.
二阶导数与凹凸性
假定在给定区间内二阶导处处存在,
• 如果在区间内 f'' > 0 on I,则函数图像向上凹(cancave up);
• 如果在区间内 f'' < 0 on I,则函数图像向上凸(cancave down);
如果二阶导数在C点改变符号,由正变负,或者由负变正,则C点为函数的拐点。
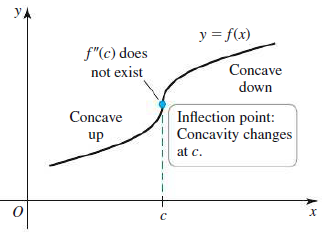

备注 ( 求inflection point在AS阶段不作要求 )
Second Derivative Test
二阶导数测试
We need to use the second derivative to identify local maxima and minima.
同学们需要掌握用二阶导数测试来确定函数的相对极值。
Second Derivative Test for Local Extrema
Suppose that f'' is continuous on an open interval containing c with f' ( c)=0.
• If f'' > 0, then f has a local minimum at c .
• If f'' < 0, then f has a local maximum at c .
• If f'' = 0, then the test is inconclusive; f may have a local maximum, local minimum, or neither at c.
假设函数的二阶导数在指定区间内连续,且点C处一阶导数为零,
如果 f'' > 0, 则函数在C处有相对最小值;
如果 f'' < 0, 则函数在C处有相对最大值;
如果 f'' = 0, 则测试结果不确定,函数在点C可能会是相对最大值,相对最小值,或者既不是相对最大值也不是最小值。

注意:二阶导数测试与一阶导数测试的第一步一样,都是找出一阶导数为零或不存在的关键点,再用不同的方法确定关键点的性质。A-Level试卷中不会明确要求使用哪种方法,需要同学们自己决定。
常考题型讲解:
Example 1
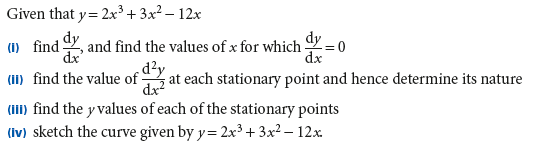
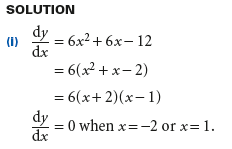
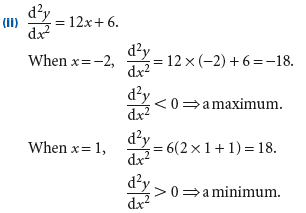
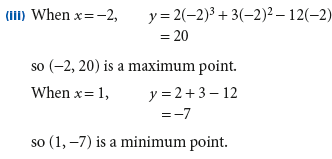
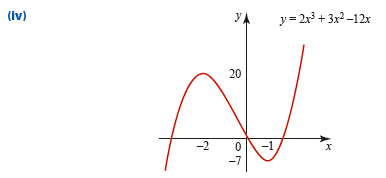
一阶导数测试与二阶导数测试的选择
一阶导数测试与二阶导数测试的目的是一样的,确定函数的相对极值性质,是最大值还是最小值。在A-Level考试中,使用一阶导数测试还是二级导数测试,取决于斜率为零的关键点的个数与函数二次求导的复杂程度。如果一阶导数为零的点较多,大于等于三个,建议使用二阶导数测试,如果阶导数为零的点只有一个或两个,且二阶导数求导复杂,可使用一阶导数测试。